Research Article
Research Methodologies in Sport Management

by James Skinner
6 February 2025
Content
Research Methodologies in Sport Management
James Skinner
Introduction
This review investigated the ten most popular sport journals in relation to their research study designs. The publications under review were published between March and September 2024. Table 1 provides a summary of the methodological approaches used in the respective journals:
Table 1: Summary of Methodological Approaches
| Journals | Mixed | Qualitative | Quantitative | Total |
| Communication & Sport | 1 |
22 (incl. 4 intros and 1 essay) |
14 | 37 |
| European Sport Management Quarterly | 3 |
29 (incl. 1 intro) |
23 | 55 |
| International Journal of Sport Finance | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| International Journal of Sport Marketing and Sponsorship | 1 | 8 | 41 | 50 |
| International Journal of Sport Communication | 1 |
35 (incl. 1 intro, 2 interviews, 1 commenatry, 1 case studies, 15 book reviews) |
9 | 45 |
| International Journal of Sport Policy and Politics | 2 |
28 (incl. two reports) |
3 | 33 |
| Journal of Global Sport Management | 3 | 14 | 12 | 29 |
| Journal of Global Sport Management | - |
1 (one obituary) |
23 | 24 |
| Journal of Sport Management | - | 9 | 12 | 21 |
| Sport Management Review | 1 | 16 | 13 | 30 |
| Overall Total | 12 | 162 | 158 | 332 |
Similar to previous reviews, qualitative and quantitative research approaches were quite balanced. Qualitative research articles were slighly more prevalent in this Sport Management Digest review, indicating a very marginal differecne as demonstrated in Figure 1.
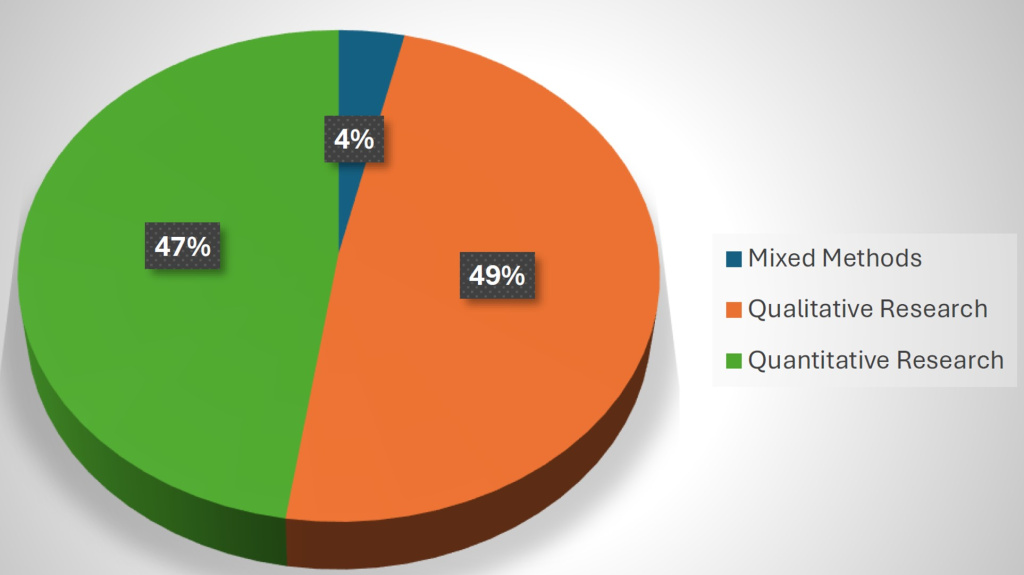
Figure 1: Distribution of Methodological Approaches
The percentage of qualitative research remained almost the same between the last six reviews and the current one.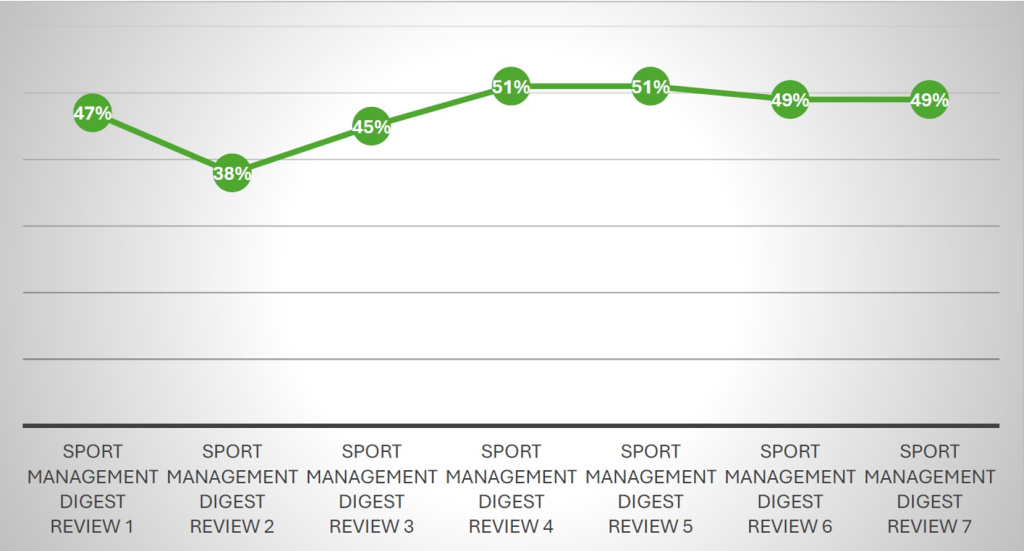
Figure 2: Sport Management Digest Review - Comparison of Qualitative Research (in %)
Also, as found in the previous reviews, a mixed method design remains somewhat under-applied, as most researchers tend to commit to either a quantitative or qualitative design. For most quantitative designs, surveys were deployed and analysed using different statistical methods. Three articles applied a Fuzzy-Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis, a technique categorised as a quantitative approach with a case-oriented character. In addition, some quantitative articles embraced the power of machine learning and utilised this approach in their data analysis.For the qualitative analyses, the most prominent approach to collecting data was grounded in (semi-structured) interviews and focus groups. Analytical approaches included thematic and content analysis. Nevertheless, other approaches such as commentaries, conceptual reviews, critical discourse analysis, phenomenology, and ethno- and netnography were also utilised.
For this review, five papers were selected for a detailed presentation. In addition, an annotated bibliography of ten papers is included at the end of this review to provide more insights into the topics and research designs deployed in the selected journals.
Success interrupted: exploring how supporters interpret their team’s success in a postponed competition (Lock et al., 2024)
This study sought to examine how Liverpool Football Club (LFC) fans perceive their team's success amid competition delays caused by COVID-19. It focused on two primary objectives. The first was to assess how fans judge success when their team's performance records remain unaffected, yet the competitive environment undergoes substantial changes, such as possible league cancellations and shifts in competition format. The second objective was to explore why winning a championship matters significantly to fans' perceptions of their in-group status, beyond merely holding a large points lead.
The researchers used a netnographic, qualitative study that analyses online discussions within specific communities to observe genuine discussions among supporters in their natural online environment. This context provided a rich understanding of how fans expressed their feelings and thoughts about their team's success amidst the uncertaintyof the league's status. Ethical clearance was obtained for the study, and the authors acknowledged the challenges of netnographic research, where forum users did not anticipate their contributions would be analysed, as such, protections were put in place. The authors analysed 15,193 posts from a LFC supporter’s fan-owned forum between 11 March and 3 June 2020. This period was chosen because it included the highest level of uncertainty regarding the team's status as potential champions due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The analysis involved a theoretical thematic approach, in which they conducted three rounds of coding to thoroughly examine the posts, focusing on how supporters discussed their team's success and the implications of the postponement.
The findings produced three key themes that illustrate how Liverpool Football Club (LFC) supporters interpreted their team's success during the postponement of the English Premier League. These themes are (1) Immortalisation of Status, where supporters felt that winning the championship would permanently solidify their status as the best team for the 2019-2020 season; (2) The Asterisk, a theme that emerged from the supporters' concerns about the legitimacy of the championship if it were to be awarded under unusual circumstances, such as the league's postponement; (3) Moments of Celebration, a theme suggesting that supporters anticipated winning the championship would create a moment of collective celebration, uniting players, coaches, and fans in a shared experience of joy and solidarity. Overall, the results indicate that context plays a significant role in how supporters evaluate their team's success, revealing that winning a championship is not just about objective performance but also about the subjective experiences and emotions tied to that success.
Exploring Perceptions of Performance Support Team Effectiveness in Elite Sport (Stewart et al., 2024)
Elite sport organisations are increasingly recruiting sophisticated performance support teams to optimise athlete performance. These teams commonly comprise sports medicine and sports science personnel (e.g. physiotherapists, sport scientists, strength and conditioning coaches, nutritionists, psychologists). Whilst the multidimensional nature of team effectiveness has been investigated in other domains, research on performancesupport teams in elite sport is sparse. This study aimed to understand how performance support teams function effectively in elite sports.
The researchers employed a phenomenological study design to examine the experiential and lived dimensions of team effectiveness among performance support team members within elite sports. This methodological approach was deemed appropriate for elucidating the nuanced and subjective factors that influence team dynamics and overall efficacy, thus facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Eighteen participants were purposely selected, all of whom engage with elite athletes or teams across a range of sports, including English Premier League Football, Formula One, and the Summer and Winter Olympic Games. The focus groups, comprising members from the same team, were intentionally homogenous to mitigate potential conflict during discussions. A semi-structured interview guide piloted before implementation directed the discussions across four key themes: team understanding, team structure and composition, processes influencing effectiveness, and facilitators and barriers to effectiveness. The data analysis process involved verbatim transcribing digitally recorded sessions, followed by reflexive thematic analysis, utilising QSR NVivo 12 software.
The inductive approach employed in this analysis prioritised researchers' reflective and interpretive engagement, identifying four predominant themes and associated sub-themes pertinent to team effectiveness. The analysis revealed four principal themes deemed essential to the effectiveness of performance support teams: (1) Team Structure: The findings indicate that a judicious balance of diversity and homogeneity among team members is crucial. A strong preference for a non-hierarchical, horizontal organisational framework was emphasised; (2) Team Member Attributes: This theme encompasses attributes such as role proficiency, open-mindedness, adaptability, and humility; (3) Shared Mental Model: This includes elements such as shared objectives, comprehension of roles, and contextual awareness; (4) Social Capital: This theme encompasses trust, respect, cohesion, and communication. The study concludes that a comprehensive understanding and proactive addressing of these four themes can significantly enhance the effectiveness of performance support teams within elite sports contexts.
Athletes’ participation in the National Anti-Doping Organisations of Germany and Poland: democratic governance? (Fiege & Zembura, 2024)
The researchers investigated the level of democratic governance in the National Anti-Doping Organisations (NADOs) of Germany and Poland, focusing on athletes’ participation within these organisations. The researchers aimed to address concerns about the lack of transparency and effectiveness in anti-doping governance and to explore how athletes’ involvement in decision-making might impact governance outcomes. The study specifically sought to assess and compare the status quo of athlete involvement in the German (NADA) and Polish (POLADA) anti-doping organisations, aiming to identify areas for improvement in fostering democratic processes.
A mixed-methods sequential explanatory design was used, incorporating document analysis and in-depth expert interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data. The document analysis evaluated selected indicators from Geeraert’s (2021a) NADGO tool, which assesses governance standards. Subsequently, expert interviews with key stakeholders provided insights into organisational practices and the challenges of enhancing athlete participation. The interview guide was grounded in academic literature and policy documents on athletes’ rights, participatory frameworks in sport governance, and anti-doping initiatives. The justification for adopting mixed methods was that its capacity to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of established governance structures and the nuanced perceptions of stakeholders ensured a thorough evaluation of democratic processes within National Anti-Doping Organizations (NADOs).
The analysis revealed differences in how NADA and POLADA approach athletes' participation, with Germany’s NADA showing a higher degree of democratic inclusion than Poland’s POLADA. NADA fulfilled more democratic governance indicators, providing athletes with voting rights on supervisory boards and incorporating their feedback into policy debates. In contrast, POLADA’s involvement of athletes was less formalised and relied more on advisory roles with limited decision-making power. The findings highlight challenges related to athletes’ resources, the institutionalisation of representation, and operational independence in enhancing democratic governance across national anti-doping frameworks.
Targeted Social Media Harassment: A Comparative Analysis of Toxicity Directed at Men and Women Sports Reporters (Johnson et al., 2024)
The research examined the challenges women sports journalists encounter online, particularly on platforms like X (formerly Twitter). This inquiry originated from recognising that women in sports journalism experience harassment that is unique in both magnitude and nature, often shaped by societal expectations and gender biases. The researchers sought to explore variations in the frequency, nature, and content of harmful posts directed at male versus female sports reporters. Their goal was to address a gap in comparative studies by determining whether women sports reporters face greater or distinct forms of toxicity compared to their male peers.Researchers performed network analysis alongside comparative quantitative content analysis of sports reporters, focusing on women and men with substantial national followings. They examined nearly 350,000 Twitter mentions over 12 years, employing a stratified random sampling method to ensure both genders were equitably represented among journalists. The team utilised Google’s Perspective API to evaluate the toxicity of the tweets, which assigns a score between 0 and 1, indicating the likelihood of toxicity (with a higher score indicating more toxicity). Furthermore, a network analysis was conducted using the Leiden algorithm to delve into the social dynamics surrounding toxic behaviour. The methodology prioritised quantifying the occurrence and context of toxic mentions while exploring differences in toxicity levels and themes based on the journalist's gender. By integrating network analysis and the Perspective API, the researchers thoroughly investigated toxicity's qualitative and quantitative aspects, shedding light on how gender impacts online harassment in sports journalism. The choice of methods was justified to maintain consistency in data collection, representation, and analysis, acknowledging that online toxicity is a complex issue that can vary significantly with audience dynamics and journalist characteristics.
The results revealed no significant difference in the percentage of toxic posts directed at male and female sports reporters; however, the content of these toxic mentions varied sharply by gender. Posts targeting male reporters were often linked to sports-related themes. In contrast, those aimed at female reporters frequently included references to gender, sexual assault, and derogatory comments on appearance or credibility.
Sports ambassadors and destination image: a fuzzy set analysis (Vila-López et al., 2024)
Vila-Lopez et al. (2024) wanted to understand the impact of sports ambassadors on a country's image as a tourism destination. They aimed to identify the essential traits that enable sports celebrities to enhance a destination’s appeal, focusing specifically on Spain. The research centred around three primary questions: which traits are the most influential in shaping a destination's image, whether these traits vary across different product categories, and whether there are significant differences in perceptions between tourists and locals. By addressing these questions, the authors intended to offer insights that could help destination marketing organisations utilise the influence of sports ambassadors to cultivate a favourable national image.
The researchers conducted a fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) with 187 participants, including tourists and residents. fsQCA combines qualitative and quantitative data to identify causal conditions leading to specific outcomes. Unlike traditional correlation-based methods, it uses set-theoretic relationships and Boolean logic to examine various factors influencing Spain's destination image. fsQCA captures the complexities of real-world scenarios and supports "equifinality," showing that different factors can yield the same outcome, thereby highlighting diverse pathways to a positive destination image. This method enabled the researchers to pinpoint particular configurations of attributes, such as trustworthiness, expertise, and attractiveness, across various sports categories, including football, tennis, and marathon running. Each participant completed a questionnaire designed to measure their perceptions of these attributes, which were calibrated to assess their significance in shaping the image of Spain. The application of fsQCA was justified based on its ability to integrate qualitative data and acknowledge various pathways to attain the same outcome, accurately representing the complexity involved in destination image formation.
The results revealed that specific attributes of sports celebrities were critical to enhancing Spain’s image, with trustworthiness and expertise emerging as the most important across all sports categories. Attributes related to attractiveness were generally less significant and, in some cases, even counterproductive. Football players were identified as the most influential in shaping Spain’s image, particularly for tourists, while marathon runners held significance for residents.
Annotated Bibliography
1. Yoo, J. J., Min, B., & Koh, Y. (2024). Cross-national news narratives of the Paralympic games: Computational text analysis of the media coverage in the United States and South Korea. Communication & Sport, 12(2), 230-253.The study investigated how media coverage of the Paralympic Games in the United States and South Korea reflects national cultural values, specifically individualism in the U.S. and collectivism in South Korea. Researchers collected two decades of news articles about the Paralympics from major newspapers in both countries. They used Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) topic modelling to identify themes and patterns in the coverage. They found that U.S. media emphasised narratives of individual athletes overcoming disability, known as the “supercrip” narrative, aligning with an individualistic cultural orientation. In contrast, South Korean media highlighted government support for the Paralympics as part of national efforts, promoting a collective image. This study contributed to cross-cultural media analysis by showing how cultural values influence representations of athletes with disabilities, and it underscores the potential of computational analysis in revealing thematic trends across large data sets.
2.Tickell, S., Sobral, V., & Meier, H. E. (2024). Finding a niche in digital plenitude: Sport media strategies of smaller European football leagues. European Sport Management Quarterly, 24(4), 876-897.
This paper investigated the impact of digital disruption on the sports media landscape, focusing particularly on smaller European football leagues. It addressed these leagues' challenges, such as increased global competition and evolving consumer behaviours. By conducting a comparative case study involving eight leagues, the authors employed document analysis and expert interviews to assess how they have adapted their business models to account for digital transformation. Key strategies include collective marketing of overseas rights, leveraging local cultural significance, and diversifying media channels. Despite their limited resources, findings showed that these leagues are creating a hybrid model that balances traditional broadcasting partnerships with innovative digital approaches like streaming and selling betting rights. The study emphasised these leagues' need to cultivate a “digital mindset” and maintain flexibility in an unpredictable future sports media environment.
3. Sun, J. Y. (2024). Free Agent Migration in the Korean Professional Baseball League: To Move or Not to Move. International Journal of Sport Finance, 19(2), 89–109. https://doi.org/10.32731/IJSF/192.052024.02
Sun (2024) examined free agent migration in the Korean Professional Baseball League (KBO) and utilised an econometric probit model to analyse data from 2000 to 2018, focusing on pitcher and hitter mobility patterns. They classified players as pitchers or hitters and used a binary dependent variable to measure the probability of a free agent moving teams. Variables included player characteristics (e.g., age, handedness), performance metrics (such as WAR), contract factors (e.g., length, signing bonuses), and team attributes like home city population and revenue. To enhance robustness, the model specifications were tested with alternative performance measures, including past WAR ratios. The study also explored the influence of market size and financial compensation on mobility, revealing significant findings on contract length, signing bonuses, and player productivity as predictors of transfer decisions.
4. Jorgensen, M. P., Hagopian, M. A., Mainwaring, L., & O'Hagan, F. T. (2024). Match official experiences with the blue card protocol in amateur rugby: Implementing rowan’s law for concussion management. International Journal of Sport Policy and Politics, 16(2), 291-306.
This research on the Blue Card protocol in amateur rugby employed Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis (IPA) to explore the experiences of six Canadian rugby match officials with this concussion management tool. The researchers conducted semi-structured interviews, directing participants through discussions on concussion awareness, the Blue Card protocol, and risk management within rugby. Data analysis adhered to a five-stage IPA process, where researchers coded and progressively refined emerging themes like "Community Engagement" and "Comfort with the Blue Card." The findings suggested support and resistance patterns in the rugby community and assessed how personal experiences and liability issues impacted officials’ comfort levels.
5. .O'Reilly, N., Paras, C., Gierc, M., Lithopoulos, A., Banerjee, A., Ferguson, L., & Faulkner, G. (2024). Nostalgia-based marketing campaigns and sport participation. International Journal of Sports Marketing and Sponsorship, 25(3), 664-683.
This study used an exploratory sequential mixed-methods approach to investigate how nostalgia-based marketing influences sports participation. Initially, they conducted aqualitative secondary analysis of five focus groups with diverse demographics to collect unprompted insights regarding nostalgic connections to ParticipACTION's Body Break campaign. This analysis informed the creation of a quantitative survey in the second phase, which was distributed online to 1,475 adults across Canada. Through path analysis, the researchers tested a model to understand the relationships among nostalgia, brand resonance, and sports engagement. This systematic two-stage design facilitated a deep thematic analysis, followed by extensive statistical validation, highlighting how effective nostalgia can be in encouraging physical activity among different generational groups.
6. Kim, K. (2024). Conceptualization and Examination of the Push-Pull-Mooring Framework in Predicting Fitness Consumer Switching Behavior. Journal of Global Sport Management, 9(1), 39–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/24704067.2021.2013128
Kim (2024) utilised a mixed-methods sequential design grounded in the push-pull-mooring (PPM) framework to examine fitness consumer switching behaviour. Study 1 employed qualitative open-ended questions to identify relevant push (negative factors of current services), pull (positive alternatives), and mooring (factors deterring switching) influences specific to fitness centres, resulting in a higher-order reflective-formative PPM model. Study 2 followed with a quantitative analysis, utilising a two-wave survey to test the relationships within the PPM framework empirically. Partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) was applied to measure the impact of these factors on actual switching behaviour and to assess mooring effects as moderators. This design contextualised the PPM framework, providing insights into fitness consumer loyalty and migration drivers. The study found that push and pull factors significantly increased the likelihood of switching behaviour among fitness consumers, while mooring effects reduced this likelihood and moderated the influence of push and pull factors, indicating that strong attachments to current fitness centres can mitigate switching even when consumers perceive better alternatives.
7. Li, J., Sun, S., & Ho, M. S. (2024). Immediate Impacts of Air Pollution on the Performance of Football Players. Journal of Sports Economics, 25(6), 753–776. https://doi.org/10.1177/15270025241260031
To analyse the immediate impacts of air pollution on football player performance in the Chinese Football Association Super League, Li et al. (2024) employed a two-stage least squares instrumental variable (IV) approach. Using air pollution data from monitoring stations combined with game data from 1,440 matches between 2014 and 2019, the researchers estimated the causal effects of pollution on player productivity, measured primarily through the number of passes. The IV approach used wind direction and long-range pollution transmission as instruments to address potential endogeneity issues. Findings indicated that a 1% increase in air pollution led to a 0.101% reduction in passes, with significant variation based on player fitness and home-field advantage.
8. Sveinson, K., & Macaulay, C. D. (2024). Selling Gender Through Kids’ Sport Team Merchandise: A Multimodal Critical Discourse Analysis. Journal of Sport Management, 38(4), 240-256. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsm.2023-0114
Recent research on team-branded fan apparel has started to reveal the communicative meanings associated with fan clothing, focusing on its gendered aspects. The study built on earlier work by analysing children's sport fan apparel through a social semiotics lens. The authors examined 377 items from 14 teams across seven major U.S. leagues. Utilising a feminist perspective and multimodal critical discourse analysis, it reveals how organisational practices and frameworks are expressed through the discourses and meanings found in the marketing of these products. The findings highlighted the existence of both gender-segregated and seemingly gender-neutral discourses, along with notions of "good parenting" that suggest purchasing these items reflects parenting values. The study concluded that to promote gender equity and inclusivity, sports organisations need to critically evaluate their internal gendered practices to align their marketing materials and products with these objectives.
9. Pape, L., Koenigstorfer, J., & Casper, J. (2024). Sport teams’ promotion of plant-based food consumption among fans. Sport Management Review, 27(1), 150–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/14413523.2023.2259146
Using a two-part survey methodology, Pape et al. (2024) analysed the influence of sports teams’ promotion of plant-based diets on fans’ sustainable food choices. In Study 1, 799 fans from 12 teams with environmental food initiatives were surveyed to measure awareness of these initiatives, fan-team personality alignment, and team value internalisation. Study 2 employed an experimental survey design, manipulating teamidentification levels among 356 fans of a single team (Boston Red Sox) to assess how varying identification impacts awareness and plant-based consumption. The findings revealed that fans with strong team identification were more likely to align with the team’s sustainable food practices. In contrast, lower identification levels correlated with a perceived personality gap, negatively impacting plant-based consumption despite high initiative awareness.
10. Carlini, J., Thomson, A., O’Neil, A., & Green, A. (2024). Understanding the interplay between event communications and local business decision-making using signalling theory: the case of the 2018 Commonwealth Games. European Sport Management Quarterly, 24(2), 428–448. https://doi.org/10.1080/16184742.2022.2125996
This study investigated the influence of event communications on local business decision-making during the 2018 Commonwealth Games. Utilising signalling theory, Carlini et al. (2024) analysed the impacts of messages by conducting 38 in-depth interviews with Gold Coast business professionals from various sectors, including tourism, hospitality, and property development. Through inductive thematic analysis with NVivo software, they identified patterns in business perceptions and their responses. The study examined how the event's information asymmetry affected businesses’ ability to leverage the Games. It revealed that exaggerated forecasts and vague messaging led to unrealistic expectations, often causing operational losses. The findings suggest that enhancing the quality of event information and its contextual relevance could improve the effectiveness of future event-driven economic strategies.
References
Carlini, J., Thomson, A., O’Neil, A., & Green, A. (2024). Understanding the interplay between event communications and local business decision-making using signalling theory: the case of the 2018 Commonwealth Games. European Sport Management Quarterly, 24(2), 428–448. https://doi.org/10.1080/16184742.2022.2125996Fiege, L., & Zembura, P. (2024). ‘Athletes’ participation in the National Anti-Doping Organisations of Germany and Poland: democratic governance?’. International Journal of Sport Policy and Politics, 16(1), 93–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/19406940.2024.2306331
Johnson, R. G., Al-khateeb, S., Forbes, A., & Cupido, K. (2024). Targeted Social Media Harassment: A Comparative Analysis of Toxicity Directed at Men and Women Sports Reporters. Communication and Sport, 12(3), 443–465. https://doi.org/10.1177/21674795231213330
Jorgensen, M. P., Hagopian, M. A., Mainwaring, L., & O’Hagan, F. T. (2024). Match official experiences with the Blue Card protocol in amateur rugby: implementing Rowan’s Law for concussion management. International Journal of Sport Policy and Politics, 16(2), 291–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/19406940.2023.2290111
Kim, K. (2024). Conceptualization and Examination of the Push-Pull-Mooring Framework in Predicting Fitness Consumer Switching Behavior. Journal of Global Sport Management, 9(1), 39–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/24704067.2021.2013128
Li, J., Sun, S., & Ho, M. S. (2024). Immediate Impacts of Air Pollution on the Performance of Football Players. Journal of Sports Economics, 25(6), 753–776. https://doi.org/10.1177/15270025241260031
Lock, D., Delia, E., Inoue, Y., & Gillooly, L. (2024). Success interrupted: exploring how supporters interpret their team’s success in a postponed competition. European Sport Management Quarterly, 24(5), 1070–1089. https://doi.org/10.1080/16184742.2023.2251999
O’Reilly, N., Paras, C., Gierc, M., Lithopoulos, A., Banerjee, A., Ferguson, L., Lee, E. Y., Rhodes, R. E., Tremblay, M. S., Vanderloo, L., & Faulkner, G. (2024). Nostalgia-based marketing campaigns and sport participation. International Journal of Sports Marketing and Sponsorship, 25(3), 664–683. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSMS-07-2023-0141
Pape, L., Koenigstorfer, J., & Casper, J. (2024). Sport teams’ promotion of plant-based food consumption among fans. Sport Management Review, 27(1), 150–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/14413523.2023.2259146
Stewart, P., Fletcher, D., Arnold, R., & McEwan, D. (2024). Exploring perceptions of performance support team effectiveness in elite sport. Sport Management Review, 27(2), 300–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/14413523.2023.2284987
Sun, J. Y. (2024). Free Agent Migration in the Korean Professional Baseball League: To Move or Not to Move. International Journal of Sport Finance, 19(2), 89–109. https://doi.org/10.32731/IJSF/192.052024.02
Sveinson, K., & Macaulay, C. D. (2024). Selling Gender Through Kids’ Sport Team Merchandise: A Multimodal Critical Discourse Analysis. Journal of Sport Management, 38(4), 240-256. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsm.2023-0114
Tickell, S., Sobral, V., & Meier, H. E. (2024). Finding a niche in digital plenitude: sport media strategies of smaller European football leagues. European Sport Management Quarterly, 24(4), 876–897. https://doi.org/10.1080/16184742.2023.2218868
Vila-López, N., Küster-Boluda, I., Aragonés-Jericó, C., & Sarabia-Sánchez, F. (2024). Sports ambassadors and destination image: a fuzzy set analysis. International Journal of Sports Marketing and Sponsorship, 25(3), 524–540. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSMS-11-2023-0227
Yoo, J. J., Min, B., & Koh, Y. H. (2024). Cross-National News Narratives of the Paralympic Games: Computational Text Analysis of the Media Coverage in the United States and South Korea. Communication and Sport, 12(2), 230–253. https://doi.org/10.1177/21674795221090420
